
|
7108
S. Alton Way, Unit I |
(303) 758-2728
Home > Elastomers > Elastomer Processing 1
Elastomer
Processing
Part 1
Polymerization
 The
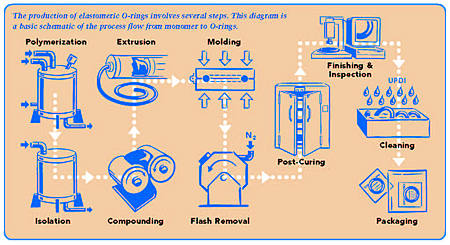
beginning step for elastomers is the polymerization of the backbone
and cure-site monomers. This is typically done by large chemical companies
such as Du Pont, GE, Ausimont, Daikin and Dyneon. Common techniques
are emulsion, microemulsion, and suspension polymerization. Polymerization
combines two or more process gases (monomers) into an aqueous environment
and under specific temperature and pressure conditions connects the
individual monomers into the desired polymer. Initiating agents, buffers
and other chemicals may be added to the polymer reactor to achieve the
desired chemical properties and polymerization dynamics.
The
beginning step for elastomers is the polymerization of the backbone
and cure-site monomers. This is typically done by large chemical companies
such as Du Pont, GE, Ausimont, Daikin and Dyneon. Common techniques
are emulsion, microemulsion, and suspension polymerization. Polymerization
combines two or more process gases (monomers) into an aqueous environment
and under specific temperature and pressure conditions connects the
individual monomers into the desired polymer. Initiating agents, buffers
and other chemicals may be added to the polymer reactor to achieve the
desired chemical properties and polymerization dynamics.
Isolation
 The
backbone polymers are isolated (brought out of the emulsion), cleaned
and dried.
The
backbone polymers are isolated (brought out of the emulsion), cleaned
and dried.
Chemical agents may be added at this step to isolate the polymer "latex" into a more usable form. Once the polymer is cleaned and dried, the "crumb" polymer is shipped to compounders (or O-ring molders) for mixing.
Compounding (mixing)
 The
"crumb" polymer is mixed with a cross-linking agent and other
functional fillers. The cross-linking agent allows chemical bonds to
form between the polymer backbones, thus providing resiliency to the
material. Functional fillers include reinforcing fillers, pigments,
anti-degradants, acid scavengers and process aids. These ingredients
are typically mixed together on a 2-roll mill or other custom mixing
machinery.
The
"crumb" polymer is mixed with a cross-linking agent and other
functional fillers. The cross-linking agent allows chemical bonds to
form between the polymer backbones, thus providing resiliency to the
material. Functional fillers include reinforcing fillers, pigments,
anti-degradants, acid scavengers and process aids. These ingredients
are typically mixed together on a 2-roll mill or other custom mixing
machinery.
Next Topic Elastomer Processing Part 2
We are located in the Denver Technological
Center in a suburb of Denver, Colorado
©1997-2017, Problem Solving Products, Inc.
Website Map | Privacy Statement
| Terms of Use

